Create a restore request
A restore request identifies the files that you want to restore from Connected to a particular device. You can create a restore request by selecting files directly from a device's backup set or an existing restore request. Requests can contain a single file or the entire backup set from an active device.
You can start a request at the time you create it or leave it pending. While a request is pending, you can add files from your backup set to it or remove files from it. Starting a request notifies the Agent to begin the restore process. If a request for a device running Agent 4.9.0, or later, contains a Windows user state (.mig) file and your backup policy allows, when starting the request, you can choose to have Connected import the file automatically after the entire restore completes.
Each time you create a restore request, regardless of whether you start it or leave it pending, Connected increments the RESTORE tab's flag. This flag indicates the total number of active restore requests that either you or your data administrator have created for your computers.  to
to  .
.
NOTE: Connected supports only one active (pending or in progress) restore request per device. You can add additional files to a device's pending request. However, if request is in progress, you cannot create another request for that device until the restore completes or you cancel it.
Before you begin
Review common restore scenarios to ensure that you understand the outcome of different types of restore requests, such as those that restore deleted items or restore files from a particular point in time. Also, if you want Connected to restore Windows user state data to a new or re-imaged computer, review the requirements to support this feature.
Create a restore request by selecting files from a backup set
Selecting files from a backup set is the most common way to create a restore request. With this method, you can restore the latest version of a device's protected file or choose a version from a previous point in time.
-
Select the backup set that contains files you want to restore:
-
(Data administrators only) To create a restore request on behalf of a user, select the user's backup set. See how.
To select the user's backup set:
-
Click the HIERARCHY tab.
-
Locate the user entry, select it, and then click VIEW (
 ).To locate the user, you can browse to the user's group, and then double-click its Users entry. However, the quickest way to find a specific user is to search by name. See how.
).To locate the user, you can browse to the user's group, and then double-click its Users entry. However, the quickest way to find a specific user is to search by name. See how.To search for a user:
-
Above the hierarchy, click Search, and then enter any portion of the user's first name, last name, or email address. The search is case insensitive.
TIP: The web application searches only the portion of the hierarchy below the currently selected item, identified by name to the left of the Search field. To search the entire hierarchy, select the entity at the very top of the hierarchy.
You can also use wildcard characters in your search criteria. See how.-
To match zero or more characters, enter an asterisk (*).
For example,
john*smithmatchesJohnSmith,john.p.smith, andjohn.paul.smith. -
To match a single character, enter a question mark (?).
For example,
john.?.smithmatchesjohn.p.smith, but notjohn.paul.smith.
As you type, the list updates to display the users that match your text.
-
- To clear the search and return to the previous view, click
 .
.
-
-
Under Sync Files and Devices, click the tile of the backup set that want to restore.
-
-
To create a restore request for your own device, click the FILES tab, and then click the BACKUP tile for that device.
-
-
To see the selected backup set from a previous point in time, in the View files as of area, set a specific date and time.
Viewing files from a previous point in time makes it easier to add multiple files as they existed at a specific point in time, such as from earlier in the day or from a previous day.
-
Find the files and folders that you want to restore:
- To restore a deleted item, under VIEWING, click Active and Deleted Items.
-
Browse for items or search for them by name. See how.
To search for an item in the current folder or its subfolders:
-
Click find something in this folder, and then enter any portion of the item's name. The search is case insensitive.
You can also use wildcard characters in your search criteria. See how.-
To match zero or more characters, enter an asterisk (
*).For example,
sales*matchesSales,Sales1, andSales-West.*salesmatchesPresales. -
To match a single character, enter a question mark (
?).For example,
Sales-??matchesSales-NWbut notSales-W. -
To match an item by exact name, enclose your text in double quotes ("
text")For example,
"SalesReport.doc"matchesSalesReport.docbut notSalesReport1.docorSalesReport.docx.NOTE: When you search using only the double quotes ("") without enclosing any text in between, the system displays a bad request error. Similarly, when you search using the special character %, the system displays the request could not be completed error.
As you type, the list updates to display the items that match your text.
-
- To clear the search and redisplay all items in the current folder, click
 .
.
-
- To see previous versions of a file, select the file, and then click VERSION HISTORY (
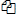 ).
).
These actions apply only to the state of the backup set that you are currently viewing. For example, while viewing the backup set from a previous point in time, a file's version history contains files only from the specified time and earlier. Any files backed up after that time are not shown because they did not exist yet.
-
Select one or more items, and then click RESTORE (
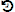 ).
). To select multiple items, press and hold either the Command (macOS) or Ctrl (Windows) key while you click each item. To select a group of contiguous items, select the first item, and then press the Shift key while you click the last item.
-
In the confirmation prompt, choose whether to add the items to a restore request and start the request now or leave it pending.
To start the request now, click START NOW. To leave the request pending so you can either add more items from your backup set to it or start it at a later time from the RESTORE tab, click LEAVE PENDING.
-
If you chose LEAVE PENDING and there are other items that you want to restore, find them in your backup set, and then add them to the request, too. There is no limit to the number of items that a restore request can contain.
NOTE: If you leave a restore request pending, the Agent does not start to restore files until you start the request.
-
If you chose START NOW, do the following:
-
If the device is running Agent version 4.6.2 or later, set the following restore options. Earlier Agents use the default restore settings.
-
Restore location. Select where the Agent restore files:
-
Original location (Default). The Agent restores files to their original location.
If the original drive or volume does not exist, the Agent restores files to
C:\From missingDriveName driveon Windows-based computers or(User's Documents Folder)/From missingDriveName volumeon macOS-based ones. -
Custom location. The Agent restores files to any folder you specify on the original device, including a mapped drive with an active connection. To specify the restore location, enter its full path. For example,
C:\Restoredon a Windows-based computers or/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restoredon a macOS-based one.If the folder you specify does not exist, the Agent creates it for you. If restoring an entire drive, the Agent restores the drive's files to the foldercustomLocation\From driveName driveon Windows-based computers orcustomLocation/From driveName volumeon macOS-based ones. See detailed examples.The following table provides examples of where the Agent restores files based on the type of item restored.
Item selected for restore Specified custom location Restored location Windows File:
D:\Reports\Sales.txtC:\RestoredC:\Restored\Sales.txtFolder:
D:\ReportsC:\RestoredC:\Restored\ReportsDrive: D:C:\RestoredC:\Restored\From D drivemacOS Folder: /Volumes/Macintosh HD/Reports/Sales.txt/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/Reports/Sales.txtAll hard disks: /or/Volumes/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/RestoredIf
/Volumescontains theMacintosh HDandPhotoshard disks:/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/From Macintosh HD volume/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/From Photos volume
Specific hard disk:
/Volumes/Photos//Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/From Photos volume
-
-
Conflicts with existing files. Select what the Agent does when it restores a file that exists:
- Keep existing files (Default). The Agent appends a number to the name of the file it restores. For example, if
Report.txtexists, the Agent renames the file it restores toReport.1.txt. - Overwrite existing files. The Agent overwrites the existing file with the one it restores.
NOTE: If you restore multiple versions of a file, the Agent always keeps the existing file regardless of whether you selected the restore option to keep or overwrite existing files. It appends the backup date to the name of each version it restores to help you differentiate between them.
- Keep existing files (Default). The Agent appends a number to the name of the file it restores. For example, if
-
Import Windows user state (Optional). If this option is available and the request contains a Windows user state
.migfile that you want Connected to import when the entire restore completes, select the option and the file to import.NOTE: If the option appears but you cannot select it, Connected is still compiling the list of
.migfiles from the restore request. Wait a minute or two, and then click the link provided to check whether the process has completed. -
File Security (Windows Only). Select, when restoring a file, whether to inherit the ACL or not.
-
Allow restoring security descriptors. By default this option is enabled. Disable this option when restoring to a non-domain windows environment. Disabling this option will not restore original file ownership details nor the ACL impacting file security.
NOTE: This option will only be displayed if the user is not part of group that allows Service Level Operations.
-
-
-
Click CONFIRM.
-
To process requests after you start them, the Agent must be running, have a network connection, and you must be logged on to the device as the user who owns the files. Otherwise, the Agent restores the files the next time these conditions are met.
To learn how to monitor a request after starting it, see How can I monitor the Agent's progress restoring files?
Create a restore request by selecting files from an existing request
Selecting files from an existing restore request is an easy way to restore specific ones again. Creating a request in this manner is especially useful after troubleshooting a restore error. For example, suppose a network issue prevents Connected from restoring some of a request's files. While viewing the request to determine which ones failed, you can quickly add those files directly to a new request instead of searching your backup set for them.
-
View the restore request that contains the files you want to restore again.
-
Select the files you want to restore. To restore all files, click SELECT ALL.
To select multiple items, press and hold either the Command (macOS) or Ctrl (Windows) key while you click each item. To select a group of contiguous items, select the first item, and then press the Shift key while you click the last item.
-
Click RESTORE (
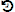 ).
).
-
In the confirmation prompt, choose whether to add the items to a restore request and start the request now or leave it pending.
To start the request now, click START NOW. To leave the request pending so you can either add more items from your backup set to it or start it at a later time from the RESTORE tab, click LEAVE PENDING.
-
If you chose LEAVE PENDING and there are other items that you want to restore, find them in your backup set, and then add them to the request, too. There is no limit to the number of items that a restore request can contain.
NOTE: If you leave a restore request pending, the Agent does not start to restore files until you start the request.
-
If you chose START NOW, do the following:
-
If the device is running Agent version 4.6.2 or later, set the following restore options. Earlier Agents use the default restore settings.
-
Restore location. Select where the Agent restore files:
-
Original location (Default). The Agent restores files to their original location.
If the original drive or volume does not exist, the Agent restores files to
C:\From missingDriveName driveon Windows-based computers or(User's Documents Folder)/From missingDriveName volumeon macOS-based ones. -
Custom location. The Agent restores files to any folder you specify on the original device, including a mapped drive with an active connection. To specify the restore location, enter its full path. For example,
C:\Restoredon a Windows-based computers or/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restoredon a macOS-based one.If the folder you specify does not exist, the Agent creates it for you. If restoring an entire drive, the Agent restores the drive's files to the foldercustomLocation\From driveName driveon Windows-based computers orcustomLocation/From driveName volumeon macOS-based ones. See detailed examples.The following table provides examples of where the Agent restores files based on the type of item restored.
Item selected for restore Specified custom location Restored location Windows File:
D:\Reports\Sales.txtC:\RestoredC:\Restored\Sales.txtFolder:
D:\ReportsC:\RestoredC:\Restored\ReportsDrive: D:C:\RestoredC:\Restored\From D drivemacOS Folder: /Volumes/Macintosh HD/Reports/Sales.txt/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/Reports/Sales.txtAll hard disks: /or/Volumes/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/RestoredIf
/Volumescontains theMacintosh HDandPhotoshard disks:/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/From Macintosh HD volume/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/From Photos volume
Specific hard disk:
/Volumes/Photos//Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/bsmith/Restored/From Photos volume
-
-
Conflicts with existing files. Select what the Agent does when it restores a file that exists:
- Keep existing files (Default). The Agent appends a number to the name of the file it restores. For example, if
Report.txtexists, the Agent renames the file it restores toReport.1.txt. - Overwrite existing files. The Agent overwrites the existing file with the one it restores.
NOTE: If you restore multiple versions of a file, the Agent always keeps the existing file regardless of whether you selected the restore option to keep or overwrite existing files. It appends the backup date to the name of each version it restores to help you differentiate between them.
- Keep existing files (Default). The Agent appends a number to the name of the file it restores. For example, if
-
Import Windows user state (Optional). If this option is available and the request contains a Windows user state
.migfile that you want Connected to import when the entire restore completes, select the option and the file to import.NOTE: If the option appears but you cannot select it, Connected is still compiling the list of
.migfiles from the restore request. Wait a minute or two, and then click the link provided to check whether the process has completed. -
File Security (Windows Only). Select, when restoring a file, whether to inherit the ACL or not.
-
Allow restoring security descriptors. By default this option is enabled. Disable this option when restoring to a non-domain windows environment. Disabling this option will not restore original file ownership details nor the ACL impacting file security.
NOTE: This option will only be displayed if the user is not part of group that allows Service Level Operations.
-
-
-
Click CONFIRM.
-
To process requests after you start them, the Agent must be running, have a network connection, and you must be logged on to the device as the user who owns the files. Otherwise, the Agent restores the files the next time these conditions are met.
To learn how to monitor a request after starting it, see How can I monitor the Agent's progress restoring files?